Change is good, change is great! This is why there will be a diversion from the normal text introduction to this particular educational hub. Please watch the short video below to begin learning about this fascinating, natural phenomenon.
What IS an earthquake and why do they occur?
What is an earthquake?
Stress within the Earth’s crust can gradually build up to form points of weakness. When the stress exerted within the rock exceeds the strength of the rock itself, it causes large fracturing along a fault line. This tension is released as huge vibrations called shockwaves. These shockwaves are the earthquake itself.
Why do they occur?
In order to explain why, we need to delve a little deeper into the Earth first. In case you haven’t found my articles entitled ‘What’s inside the Earth Part I and II’, the following will provide the basics of the structure of the Earth’s crust with reference to earthquakes.
The lithosphere is regarded as the outer shell of the Earth, and it is comprised of several, differently named tectonic plates. These plates are continually moving at a pace of a few centimetres a year. Below these lithospheric tectonic plates lies the asthenosphere. This is a more fluid layer as opposed to the rigid lithosphere. The fluidity of the asthenosphere allows the heat to convect. The convection is split into giant, convecting cells, and it is these cells that transport heat up to (and away from) the lithospheric crust.
At the tectonic plate boundaries, tremendous stresses build up when the individual plates slide past each other, or move apart. Most earthquakes occur at these plate boundaries, and most are also known to conform to the location of the Pacific Ring of Fire (the plate boundary pattern where most volcanoes are located).
More on shockwaves…
Geologically speaking, shockwaves are known as seismic waves. Seismic waves can exist as two types: P and S waves.
Primary waves
These waves are longitudinal, and the particles within the rocks travel from side-to-side (or parallel) to the direction of the wave. Imagine a slinky going back and forth; it expands and contracts and moves in one direction only. It is also a horizontal (or longitidunal) motion. P waves are faster (6-7km/sec) than S waves.
Secondary waves
S waves are transverse. This means that the particles within the rocks travel at right angles (or perpendicular) to the direction of the wave. Imagine holding the end of a rope and waving it up and down: it causes the rope to move up and down in a very typical, wave-like fashion. S waves are slower (3-4km/sec) than P waves, and cannot travel through air or liquids.
More terminology on shockwaves
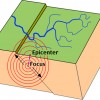
Focus or epicentre?
Seismic waves spread out from the focus. This is the exact point in the tectonic plate where the tension was released and the earthquake started.
The epicentre is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus.
Focus = starting point
Epicentre = secondary point ABOVE focus
Tectonic factsThe Mariana Trench in the western Pacific Ocean is the world’s deepest oceanic trench. It is 10,900m or 6.8 miles deep!
Mount Everest in the Himalayas is the world’s highest mountain at 8,848m above sea level.
This means that the Mariana Trench is deeper than Mt. Everest is tall!
Plate boundaries
Earthquakes can be created from a number of different plate boundary scenarios. Plate tectonics research has discovered that there are 4 seismic zones:
1) Divergent
Hot magma rises from the mantle at Mid Ocean Ridges (MORs), which pushes the plates apart. Diverge = to pull apart. The lithosphere is very thin and weak at this boundary, so the strain cannot build up enough to cause large intensity, shallow earthquakes.
2) Transform fault
This zone is not associated with any volcanic activity. Earthquakes at this boundary are caused by tectonic plates that shift past each-other in a left or right motion. Friction between the two plates can be so large that great strain can build up over time, which causes a high intensity, shallow earthquake. A classic, well-known example of this is the San Andreas fault zone in California.
3) Convergent: Continental collision
This plate boundary occurs when two slabs of continental crust plow into one another (at relatively slow geological speeds of a few centimetres per year!). The resultant force is collisional, and so forces the plates to buckle upwards and form huge mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas. Earthquakes formed here can be shallow, intermediate or deep, depending on where they occur within the plate boundary.
Shallow earthquakes occur where intense, newly formed compression is taking place. I.e.: at the birth of a new mountain range.
Deeper earthquakes happen at the base of mountain ranges, where forces have started to become subdued.
4) Convergent: Subduction zone or ‘destructive boundary’
A subduction zone is formed when an oceanic plate collides into a continental plate. When these type of plates converge, the oceanic plate is thrust underneath its continental counterpart. Oceanic crust is more dense than continental due to it being comprised of basalt.
A subduction zone forms an oceanic trench. Trenches are the deepest, darkest parts of the oceans. An earthquake can form anywhere along the subduction zone, and they can be deep, intermediate or shallow. The specialised name for where earthquakes are located along a subduction zone is called the benioff zone.
How are earthquakes measured?
Seismometers record the seismic waves that propagate from an earthquake focus. These specialised monitors are positioned at seismic recording stations across the globe. A seismometer produces a seismogram. The seismogram is the actual recording of the arrival times of P and S waves on paper.
All seismometers operate from a basic mechanism, which is the principle of inertia. I.e.: a suspended mass will lie still when the ground below it moves. The relative motion between the suspended mass and the ground will then provide a recording of the ground’s motion.
P waves are the first signal to arrive (as they are faster), followed by S waves. The distance of the recording station from the earthquake can be measured as seismologists are able to use the speed at which the wave travels, coupled with the time difference between the arrival of P and S waves. This can be summarised by the simple equation:
Distance = Speed X Time
How do seismologists accurately locate an earthquake?
Seismologists can decipher the epicentre of an earthquake by using information recording from several seismic stations. The process is called triangulation:
Signals arrive at the closest station first, and the furthest station, last.
The radii of the recording stations is drawn (computerised nowadays).
Where 3 or more radii overlap, and match up in one specific point, this is where the epicentre is located.
Mercalli or Richter scale?
There are 2 main types of scale that are used to identify the size (or magnitude) and intensity of an earthquake.
Richter
Measures the amount of energy released by the earthquake.
Is referred to as the magnitude.
This is the scale that is measured by a seismometer.
It is logarithimic, which means that a magnitude 5 is 10X greater than a 4, but 100X more powerful than a 3.
Earthquakes that are between magnitude 1-3 are not normally felt by humans, but magnitudes greater than 4 can be felt worldwide (even in Great Britain sometimes!).
Mercalli
This is completely different from the Richter as it measures the effects of the earthquake. I.e.: the intensity.
It is measured by compiling observations from humans.
The scale is from 1-12.
Economically devastating earthquakes1995: Kobe, Japan. Magnitude 6.8. 5500 killed and >26,000 injured. Economic loss of $200 billion.
1906: San Francisco, CA. Magnitude 7.8. 3000 killed, 80% of city destroyed, lasting fire damage.
2004: Indonesia. Magnitude 9. ~230,000 killed (largely from resulting tsunami).
Factors that influence earthquake magnitude and intensity
These factors cause a larger magnitude (or size) earthquake:
Relatively shallow earthquake in a tectonic plate.
Shallow ‘quakes occur at MORs, transform faults, and at the core and uppermost parts of mountain belts.
Long period of inactivity causes more stress to build up in the rock.
Previous history of large magnitude earthquakes.
Volcanic activity.
These factors cause a higher intensity earthquake:
Poorly constructed buildings that are not earthquake proof.
Non fire-resistant buildings.
Poor electrical wiring throughout a city (causes fires as a secondary impact).
Densely populated cities.
Cities that do not have an earthquake warning system.
Cities that are not economically stable and rely upon foreign aid to re-build their communities.
You may have noticed that the Mercalli scale is also influenced by the secondary effects of an earthquake. If a country is underdeveloped economically, then it will not be able to cope with the impact of an earthquake as efficiently as a more financially secure country, such as the U.K or U.S.A. Consequently, it’s recording on the Mercalli scale will be much higher.
So why are there no large earthquakes in Britain?
The island of Great Britain does not lie on a plate boundary. Neither does it lie near an active area of plate tectonic activity. However, the UK has been literally pieced together by periods of turbulent tectonic activity. These periods lasted tens of millions of years, and eventually created the Scottish Highlands, Brecon Beacons, and Peak District (among many other mountainous areas). The U.K as a whole island is a result of gradual transform (or thrust) fault activity, and collisional episodes (continental-continental collision). Even though these active periods of mountain building are long over, the rocks still contain the strain of what has once been. The strain is rarely released (as there is no active plate boundary nearby to act as a catalyst), but, when it does, it can cause an earthquake as large as a magnitude 5.
Most large (M5) earthquakes occur every 10-20 years, and are thought to be caused by previous tectonic strain, and also by regional uplift as a result of the melting of the ice sheets that once covered a substantial proportion of the UK thousands of years ago.
, Why are some earthquakes more destructive than others? www.ozeldersin.com bitirme tezi,ödev,proje dönem ödevi bitirme tezi örnekleri,tez hazırlama kuralları,tez merkezi, ,,bitirme tezi örnekleri ,bitirme tezi örneği ,bitirme tezi konuları ,örnek bitirme tezi ,lisans bitirme tezi ,lisans bitirme tezi örnekleri ,bitirme tezi indir ,bitirme tezi yazım kuralları ,endüstri mühendisliği bitirme tezi konuları ,bitirme tezi nedir ,bitirme tezi sunumu ,bitirme tezi ingilizce ,üniversite bitirme tezi ,bitirme tezi kapağı ,ktü bitirme tezi ,bitirme tezi önsöz ,tanrının bitirme tezi ,bitirme tezi pdf ,bitirme tezi örnek ,bitirme tezi kuralları ,bitirme tezi taslağı ,bitirme tezi pornosu , ,tez hazirlama ,tez hazırlama merkezleri ,tez hazırlama fiyatları ,tez hazırlama teknikleri ,tez hazırlama programı ,tez hazırlama yönergesi ,tez kapağı hazırlama ,tez içindekiler hazırlama , ,bitirme tezi nasıl hazırlanır ,bitirme tezi nasıl yazılır ,yüksek lisans tezi nasıl yazılır ,yüksek lisans tezi nasıl hazırlanır ,doktora tezi nasıl yazılır ,lisans tezi nasıl yazılır , ,tez merkezi ,tez hazırlama merkezi ,ödev tez merkezi ,türkiye tez merkezi ,tez yazim merkezi ,tez tarama merkezi ,tez araştırma merkezi ,osym tez merkezi ,tez arama merkezi ,akademi tez merkezi ,istanbul tez merkezi ,tez proje yazım merkezi ,yüksek öğretim tez merkezi , ,tez yazma ,tez yazma fiyatları ,tez yazma teknikleri ,tez yazma programı ,tez yazma kurallari , ,odev ,ödev kapağı hazırlama ,odev kapaklari ,ödev yapma siteleri ,ödev hazırlama ,tez ödev ,ödev yapılır ,ödev yapan siteler ,ödev kapakları hazırla ,odev sitesi ,ödev bul ,ödev hazırlama siteleri ,ödev bulma siteleri ,odev tez ,ödev yaptırmak istiyorum ,odev siteleri , ,yüksek lisans proje örnekleri ,yüksek lisans proje konuları ,tezsiz yüksek lisans proje örnekleri ,yüksek lisans tez ,lisans tez , ,bitirme projesi ,bitirme projesi örnekleri ,bitirme projesi örneği ,bitirme projesi konuları ,lisans bitirme projesi ,bilgisayar mühendisliği bitirme projesi örnekleri , ,tez konulari ,yüksek lisans tez konuları ,muhasebe tez konuları ,kamu yönetimi tez konuları ,psikoloji tez konuları ,ekonomi tez konuları ,halkla ilişkiler tez konuları ,maliye tez konuları ,insan kaynakları tez konuları ,bankacılık tez konuları ,dış ticaret tez konuları ,hazır tez konuları ,finans tez konuları ,endüstri mühendisliği tez konuları ,maliye bölümü tez konuları ,turizm tez konuları ,lisans tez konuları ,besyo tez konuları ,yönetim ve organizasyon tez konuları ,lojistik tez konuları ,muhasebe ile ilgili tez konuları ,istatistik tez konuları ,kimya tez konuları ,iktisat tez konulari ,doktora tez konuları ,bankacılıkla ilgili tez konuları ,biyokimya tez konuları ,ekonometri tez konuları ,bilgisayar tez konuları ,gazetecilik tez konuları ,hukuk tez konuları ,finansla ilgili tez konuları ,sosyoloji tez konulari , ,tez konusu belirleme ,tez konusu bulma ,tez konusu ,tez konusu bul ,tez konusu bulmak ,iktisat tez konusu ,tez konusu seçme ,doktora tez konusu ,tez konusu arama , ,lisans bitirme tezleri ,doktora tezleri ,lisans tezleri ,üniversite tezleri ,üniversite bitirme tezleri ,iktisat tezleri ,yuksek lisans tezleri ,pazarlama tezleri ,bitirme tezleri örnekleri ,turizm tezleri ,bankacılık tezleri ,uluslararası ilişkiler tezleri ,işletme tezleri ,araştırma tezleri ,eğitim tezleri , ,tezler ,örnek tezler ,pazarlama ile ilgili tezler ,hazir tezler ,yapılmış tezler ,bankacılıkla ilgili tezler ,ödev ve tezler ,uluslararası tezler , ,bitirme ödevi ,bitirme ödevi örnekleri ,bitirme ödevi örneği ,bitirme ödevi nasıl hazırlanır ,bitirme ödevi konuları , ,yüksek lisans tez örnekleri ,tez ornekleri ,lisans tez örnekleri ,bitirme tez örnekleri ,tez örnekleri indir ,tez anket örnekleri ,besyo tez örnekleri ,muhasebe tez örnekleri ,üniversite tez örnekleri ,sakarya üniversitesi tez örnekleri , ,tez yazim kurallari ,tez yazım kılavuzu ,tez yazım formatı ,tez yazım ,lisans tez yazım kuralları ,tez yazım programı ,ege üniversitesi tez yazım kılavuzu ,tez yazım teknikleri ,tez yazim klavuzu ,ankara tez yazım merkezleri ,yıldız teknik üniversitesi tez yazım kılavuzu ,ytü lisans tez yazım kılavuzu , ,tez nasil yazilir ,tez ödevi nasıl hazırlanır ,tez nasıl yapılır ,tez nasil hazirlanir ,tez konusu nasıl bulunur ,lisans tez nasıl hazırlanır , ,tez siteleri ,tez arama siteleri ,tez araştırma siteleri ,tez indirme siteleri ,tez bulma siteleri ,ödev tez siteleri , ,işletme tez konuları ,işletme bölümü tez konuları ,tez konuları işletme ,işletme tez konusu ,işletme yönetimi tez konuları ,işletme tez , ,doktora tezi ,lisans tezi ,lisans tezi örneği ,yuksek lisans tezi ,yüksek lisans tezi örneği ,pazarlama tezi , ,pazarlama tez konuları ,pazarlama tez konusu ,pazarlama ile ilgili tez konuları ,pazarlama tez ,pazarlama tez örnekleri , ,uluslararası ilişkiler tez konuları ,uluslararası ilişkiler bölümü tez konuları ,uluslararası tez arama ,siyaset bilimi ve uluslararası ilişkiler tez konuları ,uluslararası ilişkiler bitirme tez konuları , ,tez ,tez arama ,tez tarama ,tez indir ,tez yazan yerler ,tez yazmak ,tez nedir ,tez önerisi örneği ,tez bul ,tez ödevleri ,tez formatı ,tez yazimi ,tez sitesi ,tez arama motoru ,tez yazdırmak istiyorum ,örnek tez önerileri ,tez araştırma ,tez yazilir ,tez çalışmaları ,yok tez arama ,tez ödevi ,tez danışmanlığı ,osym tez ,tez danışmanlık ,tez ara ,tez hazırlamak ,tez bulma ,tez merkezleri ,ücretli tez yazımı ,tez proje ,örnek tez yazımı ,tez danışmanı ,tez yazdirma ,tez ornegi ,tez destek ,tez yardım ,san tez projeleri ,tez yazdırmak isteyenler ,tez başlıkları ,ornek tez ,hazır tez indir ,istanbul tez ,tez projesi ,tez bankasi ,tez yaptırma ,tez yazanlar ,tez yazdırmak ,akademik tez ,tez kapaklari ,tez hazırlanır ,üniversite tez ,hazir tez ,tez düzenleme ,proje tez ,tez önerileri ,tez analizi ,tez yapan yerler ,tez araştır ,örnek tez çalışması ,tez düzeltme ,tez ler ,bilimsel tez ,tez araştırması ,tez yazılır ankara ,ankarada tez yazan yerler ,tez yazılır istanbul ,sakarya üniversitesi tez ,tez yazımı ankara ,tez arsivi ,tez yapılır ,tez istanbul ,tez çevirisi ,tez başlığı , ,bitirme projeleri ,uluslararası ilişkiler bölümü ,lisansüstü eğitim ,iktisadi ve idari bilimler ,mezuniyet projesi ,üniversite bitirme projeleri ,yıldız teknık unıversıtesı ,elektronik bitirme projeleri ,idari bilimler fakültesi ,yıldız teknik ü ,uluslararası ilişkiler fakültesi ,yazim kilavuzuzu ,iktisadi ve idari bilimler fakultesi ,üniversite kılavuzları ,uluslararası ılıskıler derslerı , , , ,
